Publications
2025
-
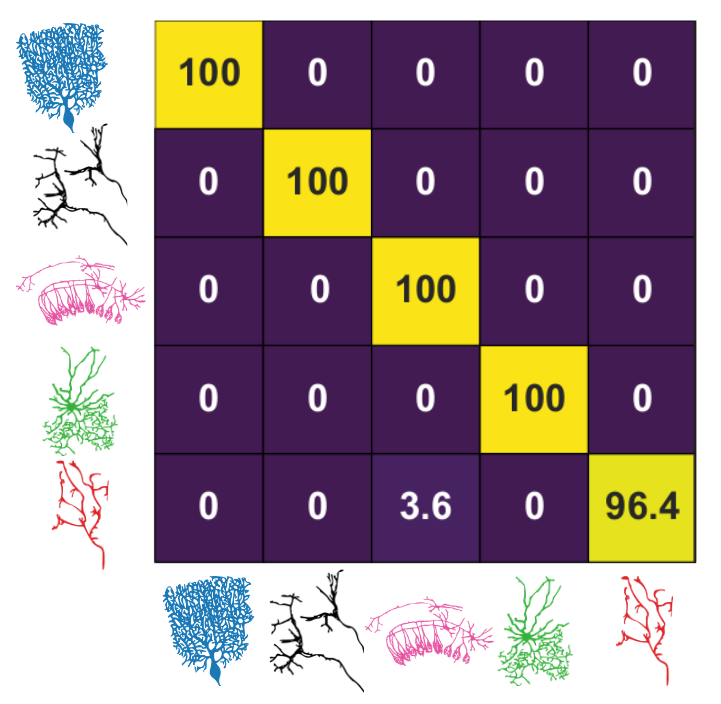 Maxime Beau, David J Herzfeld, Francisco Naveros, and 20 more authorsCell, 2025
Maxime Beau, David J Herzfeld, Francisco Naveros, and 20 more authorsCell, 2025High-density probes allow electrophysiological recordings from many neurons simultaneously across entire brain circuits but fail to reveal cell type. Here, we develop a strategy to identify cell types from extracellular recordings in awake animals and reveal the computational roles of neurons with distinct functional, molecular, and anatomical properties. We combine optogenetics and pharmacology using the cerebellum as a testbed to generate a curated ground-truth library of electrophysiological properties for Purkinje cells, molecular layer interneurons, Golgi cells, and mossy fibers. We train a semi-supervised deep learning classifier that predicts cell types with greater than 95% accuracy based on the waveform, discharge statistics, and layer of the recorded neuron. The classifier’s predictions agree with expert classification on recordings using different probes, in different laboratories, from functionally distinct cerebellar regions, and across species. Our classifier extends the power of modern dynamical systems analyses by revealing the unique contributions of simultaneously recorded cell types during behavior.
2021
-
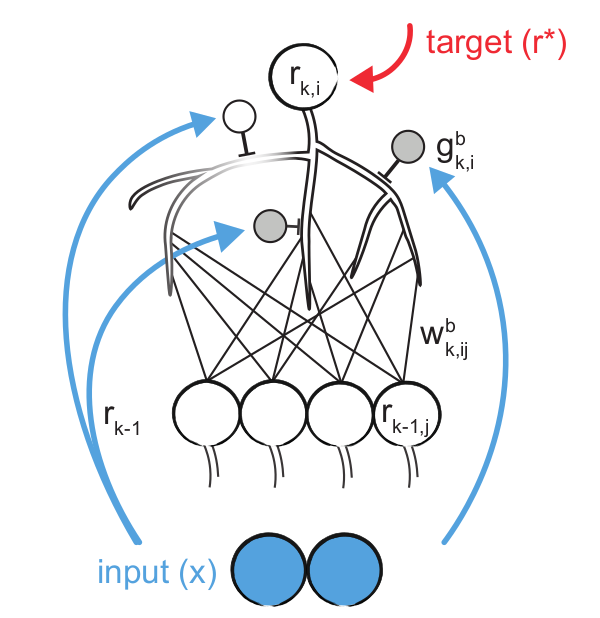 Eren Sezener, Agnieszka Grabska-Barwińska, Dimitar Kostadinov, and 8 more authorsBioRxiv, 2021
Eren Sezener, Agnieszka Grabska-Barwińska, Dimitar Kostadinov, and 8 more authorsBioRxiv, 2021The dominant view in neuroscience is that changes in synaptic weights underlie learning. It is unclear, however, how the brain is able to determine which synapses should change, and by how much. This uncertainty stands in sharp contrast to deep learning, where changes in weights are explicitly engineered to optimize performance. However, the main tool for that, backpropagation, has two problems. One is neuro-science related: it is not biologically plausible. The other is inherent: networks trained with this rule tend to forget old tasks when learning new ones. Here we introduce the Dendritic Gated Network (DGN), a variant of the Gated Linear Network, which offers a biologically plausible alternative to backpropagation. DGNs combine dendritic ‘gating’ (whereby interneurons target dendrites to shape neuronal responses) with local learning rules to yield provably efficient performance. They are significantly more data efficient than conventional artificial networks, and are highly resistant to forgetting. Consequently, they perform well on a variety of tasks, in some cases better than backpropagation. Importantly, DGNs have structural and functional similarities to the cerebellum, a link that we strengthen by using in vivo two-photon calcium imaging to show that single interneurons suppress activity in individual dendritic branches of Purkinje cells, a key feature of the model. Thus, DGNs leverage targeted dendritic inhibition and local learning – two features ubiquitous in the brain – to achieve fast and efficient learning.
-
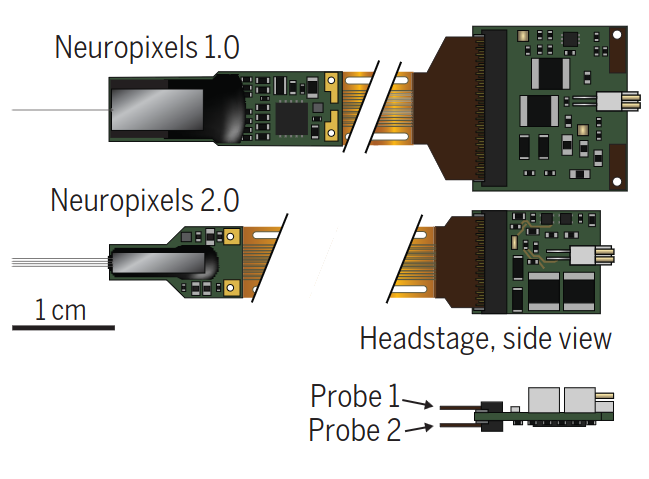 Nicholas A Steinmetz, Cagatay Aydin, Anna Lebedeva, and 8 more authorsScience, 2021
Nicholas A Steinmetz, Cagatay Aydin, Anna Lebedeva, and 8 more authorsScience, 2021The ultimate aim of chronic recordings is to sample from the same neuron over days and weeks. However, this goal has been difficult to achieve for large populations of neurons. Steinmetz et al. describe the development and testing of Neuropixels 2.0. This new electrophysiological recording tool is a miniaturized, high-density probe for both acute and long-term experiments combined with sophisticated software algorithms for fully automatic post hoc computational stabilization. The technique also provides a strategy for extending the number of recorded sites beyond the number of available recording channels. In freely moving animals, extremely large numbers of individual neurons could thus be followed and tracked with the same probe for weeks and occasionally months.
2020
-
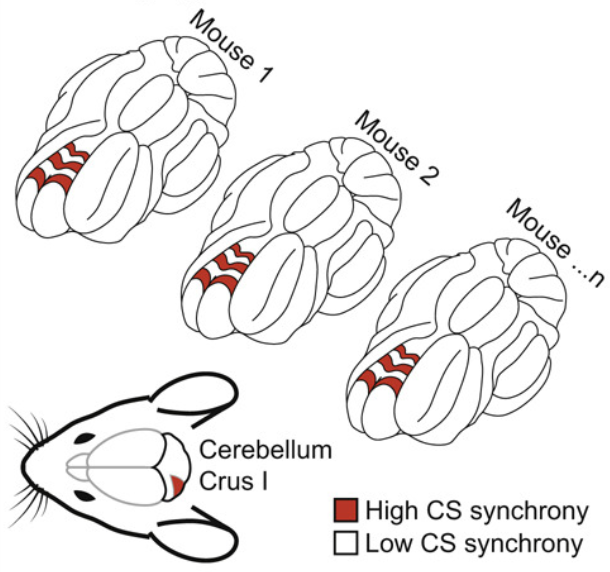 Shinichiro Tsutsumi, Oscar Chadney, Tin-Long Yiu, and 4 more authorsCell reports, 2020
Shinichiro Tsutsumi, Oscar Chadney, Tin-Long Yiu, and 4 more authorsCell reports, 2020Cerebellar neurons can signal sensory and motor events, but their role in active sensorimotor processing remains unclear. We record and manipulate Purkinje cell activity during a task that requires mice to rapidly discriminate between multisensory and unisensory stimuli before motor initiation. Neuropixels recordings show that both sensory stimuli and motor initiation are represented by short-latency simple spikes. Optogenetic manipulation of short-latency simple spikes abolishes or delays motor initiation in a rate-dependent manner, indicating a role in motor initiation and its timing. Two-photon calcium imaging reveals task-related coherence of complex spikes organized into conserved alternating parasagittal stripes. The coherence of sensory-evoked complex spikes increases with learning and correlates with enhanced temporal precision of motor initiation. These results suggest that both simple spikes and complex spikes govern sensory-driven motor initiation: simple spikes modulate its latency, and complex spikes refine its temporal precision, providing specific cellular substrates for cerebellar sensorimotor control.
2019
-
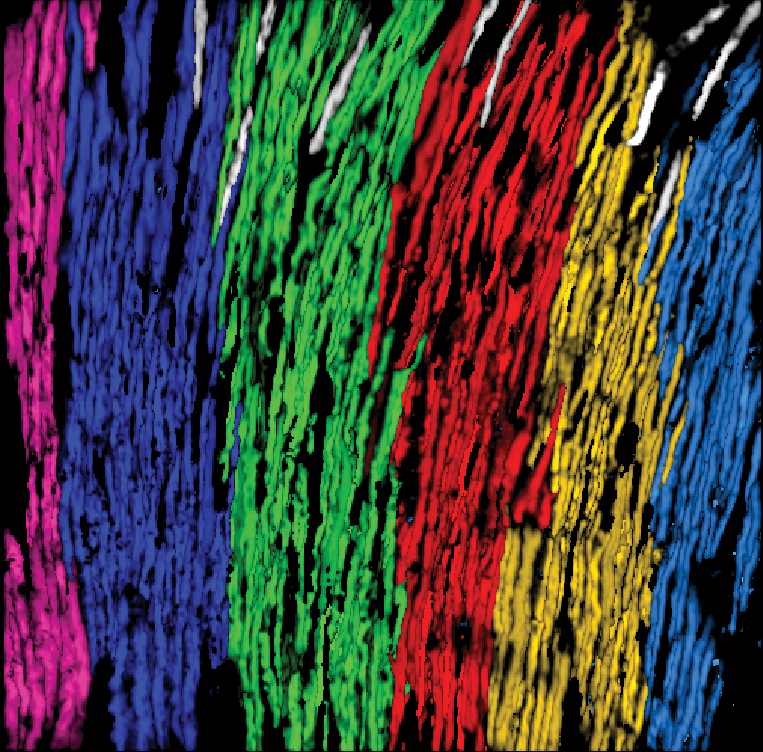 Dimitar Kostadinov, Maxime Beau, Marta Blanco-Pozo, and 1 more authorNature Neuroscience, 2019
Dimitar Kostadinov, Maxime Beau, Marta Blanco-Pozo, and 1 more authorNature Neuroscience, 2019There is increasing evidence for a cerebellar contribution to cognitive processing, but the specific input pathways conveying this information remain unclear. We probed the role of climbing fiber inputs to Purkinje cells in generating and evaluating predictions about associations between motor actions, sensory stimuli and reward. We trained mice to perform a visuomotor integration task to receive a reward and interleaved cued and random rewards between task trials. Using two-photon calcium imaging and Neuropixels probe recordings of Purkinje cell activity, we show that climbing fibers signal reward expectation, delivery and omission. These signals map onto cerebellar microzones, with reward delivery activating some microzones and suppressing others, and with reward omission activating both reward-activated and reward-suppressed microzones. Moreover, responses to predictable rewards are progressively suppressed during learning. Our findings elucidate a specific input pathway for cerebellar contributions to reward signaling and provide a mechanistic link between cerebellar activity and the creation and evaluation of predictions.